Description
The highest efficient solar panels currently are made of monocrystalline silicon, with some top-tier commercial models achieving efficiencies around 22-23%. However, in research settings, materials like perovskites have shown potential efficiencies exceeding 30%.

Types of Solar Panels
Solar panels have come a long way since their inception. As technology advances, we are presented with a variety of panel types, each with its unique properties, advantages, and applications. Let's dive deeper into the major types available in the market today.
Monocrystalline Silicon Panels
- Definition: Monocrystalline panels are made from single-crystal silicon. Because of the uniformity in their structure, they have a smooth texture and offer higher efficiencies.
- Efficiency: Typically, these panels have an efficiency of around 20%.
- Cost: On average, monocrystalline panels cost between $0.20 to $0.30 per watt.
- Advantages: High efficiency, longer lifespan (about 25-30 years), and a sleek appearance.
- Drawbacks: Higher initial cost compared to other types, and the production process can waste silicon.
Polycrystalline Silicon Panels
- Definition: These panels are made from multiple silicon crystals. They have a fragmented, or "frosted" appearance, due to the various orientations of the silicon crystals.
- Efficiency: They usually have an efficiency rate of 15-17%.
- Cost: Typically, they are priced at $0.15 to $0.20 per watt.
- Advantages: Lower initial cost and a simpler manufacturing process, which requires less energy and materials.
- Drawbacks: Slightly lower efficiency and a shorter lifespan (about 23-27 years) compared to monocrystalline panels.
Thin-film Solar Cells
- Definition: These cells are created by placing one or more thin layers of photovoltaic material onto a substrate.
- Efficiency: Their efficiency ranges from 10-12%.
- Cost: They are generally the cheapest, priced at around $0.10 to $0.15 per watt.
- Advantages: Highly flexible, lightweight, and can be integrated into building materials.
- Drawbacks: Lower efficiency, shorter lifespan (around 15-20 years), and larger size needed for the same power output.
Building-integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV)
- Definition: BIPV systems integrate solar panels directly into the building structure, such as roofs, facades, or windows, rather than being a separate system mounted on the structure.
- Efficiency: Varies based on the type of solar cell used but is generally between 15-20%.
- Cost: BIPV systems can be more expensive, ranging from $0.30 to $0.50 per watt, due to customization.
- Advantages: Aesthetic appeal, space-saving, and potential to reduce construction materials.
- Drawbacks: Higher initial cost, potential challenges in maintenance, and may not be optimal for solar orientation.
Each of these solar panel types has its role in the market based on application requirements,
budget, and desired efficiency. It's essential to understand each type's strengths and weaknesses when considering a solar energy project.
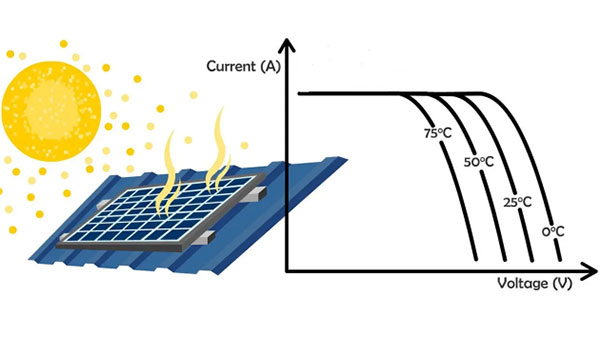
Factors Affecting Solar Panel Efficiency
Solar panel efficiency plays a pivotal role in determining how much energy a panel can produce. However, several external and inherent factors can influence this efficiency. Let's delve deeper into some key factors that impact solar panel efficiency.
| Factor |
Details |
| Temperature |
Solar panels typically perform best at cooler temperatures. As temperature rises, efficiency tends to decrease. Most solar panels see a decrease of about 0.5% in efficiency for every 1°C increase above 25°C. |
| Angle of Incidence |
The angle at which sunlight hits the solar panel plays a crucial role in its efficiency. Optimal angles vary depending on geographic location and time of year. Panels that directly face the sun at a 90-degree angle capture the most energy. |
| Dust and Debris |
Accumulation of dust, dirt, or other debris on the panel's surface can block sunlight and reduce its efficiency. Regular cleaning and maintenance help in ensuring optimal energy capture. |
| Degradation Over Time |
As solar panels age, their efficiency naturally decreases. On average, solar panels degrade at a rate of about 0.5% to 1% per year. This means after 25 years, a panel might operate at around 75%-88% of its original efficiency. |
Understanding these factors is crucial for anyone planning to invest in solar panels, as it aids in making an informed decision regarding installation,
budget, and maintenance.
Current Leaders in Solar Panel Efficiency
The race for the highest solar panel efficiency is on, as the world gravitates towards sustainable energy. As technology evolves, manufacturers constantly push the boundaries to offer panels that provide maximum power output with the smallest footprint. Here's a look at the frontrunners in this ever-evolving field.
Top Manufacturers and Their Records
- Tongwei: This brand, renowned for its innovation, has been making waves in the solar industry. With an established presence, Tongwei has produced panels with an impressive efficiency of around 23%. Apart from its high efficiency, the brand stands out for its commitment to sustainability and eco-friendly production processes.
- SunPower: Known for its high-quality solar panels, SunPower holds records with efficiencies surpassing 22%. Their panels not only boast of high efficiency but are also backed by robust warranties, ensuring longevity.
- LG: Another top contender in the efficiency race, LG’s premium panels often hit the 21-22% mark. With a blend of aesthetics and performance, their panels have become a preferred choice for many homeowners.
- Panasonic: With its HIT technology, Panasonic panels offer efficiencies in the ballpark of 21%. Their unique heterojunction technology contributes to better performance even in high-temperature conditions.
- Note: While these numbers represent some of the top achievements by these manufacturers, the average efficiency on a commercial scale might be slightly lower due to production constraints, cost considerations, and other factors.
Latest Innovations and Breakthroughs
- Tandem Solar Cells: These cells use two different types of solar materials stacked together. This structure helps capture a broader spectrum of sunlight, pushing efficiencies beyond 30% in lab conditions.
- Bifacial Panels: Panels that can capture sunlight from both the front and the rear side have emerged as a game-changer. They can produce up to 20% more power than traditional monofacial panels.
- Transparent Solar Panels: Innovators are working on panels that are transparent and can be integrated into windows or facades. While still in the developmental phase, they could revolutionize urban solar installations.
- Flexible Panels: The advent of thin, flexible panels opens up new avenues for installations. These can be rolled out or adhered to surfaces that traditional panels can't be fixed to.
- Enhanced Energy Storage: With advancements in battery technology, the potential to store solar energy has increased, allowing users to harness the sun's power even during non-sunny hours.
In a world where
sustainability is paramount, the drive for higher solar panel efficiency is relentless. Manufacturers, researchers, and innovators are continuously exploring avenues to harness the sun's power most effectively and efficiently.

Benefits of High-efficiency Solar Panels
The solar energy landscape has witnessed substantial growth over the past decade, much of which can be attributed to advancements in solar panel efficiency. High-efficiency panels are not just a marketing gimmick; they bring tangible benefits that can be seen in power generation, financial savings, and environmental protection.
More Power in Less Space
High-efficiency solar panels are often the go-to choice for urban dwellers or those with limited roof space. With an efficiency rate surpassing 20% in some models, these panels can produce:
- Power Output: A high-efficiency 300W panel with an efficiency of 22% can produce around 66W per square foot, while a regular 18% efficient panel might produce only 54W for the same space. This means for a 500 square foot installation area, you could get an extra 6000W with the high-efficiency panel.
- Space Savings: For households aiming for a 5kW system, using high-efficiency panels might save them around 80-100 square feet of installation space. This saved space can be utilized for other purposes or even future expansions.
Cost Efficiency Over Time
While high-efficiency panels might come with a steeper upfront
cost, the returns over the lifespan of the panel make it a worthy investment:
- Long-term Savings: If electricity prices average at $0.12 per kWh, and you're producing an extra 6000W due to higher efficiency, that's an added savings of approximately $720 annually.
- Resale Value: Homes equipped with high-efficiency solar installations often see an increase in resale value, making it a lucrative long-term investment.
- Reduced Energy Bills: Efficient panels often mean reduced reliance on grid electricity, translating to significant monthly and yearly savings.
Environmental Impact Reduction
Solar energy's primary appeal lies in its green credentials, and efficient panels amplify this benefit:
- Carbon Footprint: By producing more power with fewer panels, you reduce the need for extensive manufacturing processes. This means that for every high-efficiency panel made, there's less carbon footprint compared to producing multiple low-efficiency ones.
- Resource Conservation: Efficient panels use cutting-edge materials and technology. These materials often require less raw material extraction, leading to reduced strain on natural resources.
- Waste Reduction: As efficient panels last longer and require fewer replacements, there's a consequent reduction in waste generated from old panels.
In essence, while the immediate allure of high-efficiency panels might be their power output, their long-term benefits, both financial and environmental, make them an optimal choice for a sustainable future.
The Future of Solar Panel Efficiency
Solar energy, already a beacon of hope for sustainable power solutions, is on the cusp of revolutionary changes. As we enter an era dominated by technological advancements and increased environmental awareness, the solar industry is poised to benefit from both. By understanding the trajectory of solar panel efficiency, we can glimpse the solar-dominated world of the future.
Upcoming Technologies and Research Areas
While we've made significant strides in solar efficiency, there's still plenty of room for growth. Current top-tier commercial panels boast efficiencies around 22-23%, but cutting-edge research hints that this number could rise substantially. For instance:
Perovskite Solar Cells: These have emerged as one of the most promising materials for future solar tech. Perovskites are not only cheap and easy to produce but have shown efficiency potentials exceeding 30% in lab settings. If commercialized successfully, they could offer a substantial reduction in solar panel
cost while providing high power output.
Quantum Dot Solar Cells: Another promising avenue of research, quantum dots are nano-sized semiconductors that can enhance solar cell efficiency. Their capacity to absorb different parts of the solar spectrum makes them invaluable. Though still in the research phase, they promise efficiencies that could rival or even surpass perovskites in the future.
Light Manipulation Techniques: By manipulating light at a nano-scale using structures like photonic crystals, researchers aim to direct more sunlight into solar cells, which could lead to much higher efficiencies.
Predictions for the Next Decade
The next ten years will be transformative for solar energy. Here's what we can expect:
Breaking the 30% Commercial Barrier: With advancements in materials like perovskites and quantum dots, we're likely to see commercial panels breaking the 30% efficiency barrier. This would mean that a single square meter of solar panel could produce up to 300W of power, a significant improvement from today's average of 180-200W.
Reduction in Solar Energy Costs: As efficiency increases, the cost per watt of solar installations will decrease. It's feasible that, given the current rate of technological advancement and economies of scale, solar energy could become one of the cheapest forms of electricity generation.
Widespread Adoption: As prices drop and efficiency rises, solar energy will become accessible to millions more people around the world. This mass adoption will not only reduce global carbon emissions but also help in energy independence for many nations.
Innovation in Material Lifespan: Current solar panels have a lifespan of around 25-30 years. With ongoing research, we might see panels that not only have higher efficiencies but also last 40 years or more, ensuring even longer-term benefits from a single installation.
In conclusion, the future shines bright for solar panel efficiency. With relentless research and a global push towards sustainability, solar energy is set to play a pivotal role in the global energy matrix. The next decade will not only witness enhanced efficiency but also a more widespread adoption of this clean and abundant source of energy.







