Description
Yes, solar panels are likely to become cheaper in 2024 due to technological advancements, economies of scale, and increased competition in the market.

Factors Influencing Solar Panel Prices
The solar industry has witnessed dramatic shifts in pricing over the years, driven by a combination of technological, economic, and global supply chain factors. Understanding these elements is crucial for both industry insiders and consumers looking to leverage solar energy.
Technological Advancements and Efficiencies
With the relentless pace of
technological advancement, solar panels have seen significant improvements in their efficiency and functionality.
- Efficiency Rates: Modern solar panels, for instance, boast efficiency rates of around 18-22%. Just a decade ago, these figures lingered around 15%. This means that today's panels can generate more energy from the same amount of sunlight.
- Size and Specifications: Despite their increased efficiency, the size and specifications of solar panels have largely remained consistent. A standard solar panel measures approximately 65 inches by 39 inches.
- Materials: Innovations in materials used, like the transition from polycrystalline to monocrystalline silicon, have played a pivotal role. Monocrystalline panels, with their single-crystal structure, are generally more efficient than their polycrystalline counterparts.
- Lifespan and Age: The average lifespan of solar panels has also been on the rise. Most panels come with a 25-year warranty, but many can last 30 years or more, which speaks to their enhanced quality and durability.
Economies of Scale and Mass Production
As with many products, producing solar panels on a larger scale leads to cost savings – a principle known as
economies of scale.
- Production Costs: The cost to produce a solar panel has plummeted over the years. In the early 2010s, the cost was roughly $0.70 per watt. Now, that figure hovers around $0.20 per watt.
- Advantages of Mass Production: Manufacturers have optimized their processes, reducing waste and speeding up production times. As a result, they can produce more panels at a fraction of the initial cost.
- Budget and Pricing: Because of these cost savings, the price consumers pay for solar panels has also decreased, making solar energy more accessible to the masses.
Global Supply Chain Dynamics
The global
supply chain for solar panels is intricate and has its set of challenges and advantages.
- Raw Material Availability: The availability and price of raw materials can fluctuate, affecting the cost of the end product. For example, a shortage of silicon, a primary component of solar panels, can drive up prices.
- Trade Policies: Import tariffs and trade restrictions can significantly impact costs. For instance, tariffs on solar panels imported into the U.S. in recent years increased prices temporarily.
- Manufacturing Hubs: Regions like China have become powerhouses in solar panel manufacturing, capitalizing on cheaper labor and materials. This concentration can lead to competitive pricing but can also create vulnerabilities in the supply chain, especially if there are disruptions in a particular region.
In summary, while numerous factors play into the cost of solar panels, continuous innovations and global market dynamics seem to be pushing prices downwards, benefiting end-users.
Predictions for Solar Panel Prices in 2024
The future of solar panel pricing is a topic of intense interest for both industry professionals and environmentally conscious consumers. While it's difficult to pin down exact figures for 2024, several factors can give us insight into potential trends.
Industry Expert Opinions
Leading voices in the solar industry continually analyze market data to forecast future prices. Here's what some of them have been saying:
- Growth in Technology: Experts anticipate a steady rise in the efficiency of solar panels, potentially reaching up to 24% by 2024. This increase would mean that solar installations would require fewer panels, thus potentially reducing costs.
- Quality over Quantity: Some industry leaders predict a shift in focus from sheer production volume to the quality of solar panels. This might mean slightly higher prices for top-tier panels but longer lifespans and better performance.
- Price Points: According to various market analyses, the price per watt could fall to around $0.18 by 2024, a modest reduction from current rates but significant when considering large installations.
Government Incentives and Subsidies
Governments worldwide have recognized the
value of solar energy, not just as a renewable energy source but also as a means to create jobs and stimulate economic growth.
- Tax Breaks and Rebates: Many countries offer tax incentives for installing solar panels. For example, the US has extended the Solar Investment Tax Credit, which allows homeowners and businesses to deduct a portion of the cost of installing a solar system from their taxes.
- Grants and Subsidies: Some regions provide direct subsidies or grants to reduce the upfront cost of solar installations. These can significantly affect the final price consumers pay.
- Feed-in Tariffs: In places with feed-in tariffs, consumers can sell excess solar energy back to the grid. This not only reduces the overall cost of solar panel ownership but can also turn it into a profitable venture over time.
Market Demand and Consumer Adoption
The demand for solar panels is intrinsically linked to its price. As prices fall, demand generally rises. However, several factors could influence this dynamic.
- Awareness and Education: As more people become aware of the environmental and economic benefits of solar energy, demand is likely to increase, potentially leading to economies of scale and reduced prices.
- Alternative Energy Sources: The rise of other renewable energy sources, such as wind or hydroelectric power, might influence solar panel demand. If these alternatives become cheaper or more accessible, they could pose competition.
- Installation Costs: While the cost of the panels themselves is crucial, the cost of installation can't be ignored. If installation becomes faster or requires fewer resources, the overall price of getting a solar system up and running could decrease.
In summary, while predicting exact prices in 2024 is challenging, the intersection of expert opinions, government policies, and consumer behavior offers a promising outlook for the affordability and adoption of solar panels.

Comparing 2024 Predictions with Previous Years
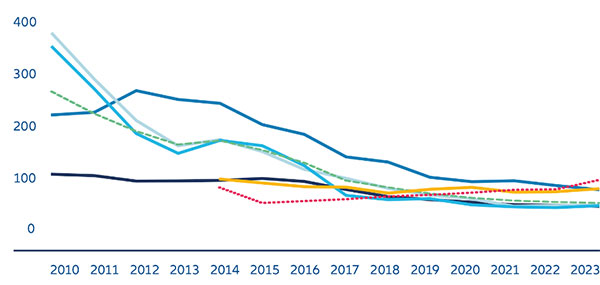
Analyzing predictions for solar panel prices in 2024 requires us to look back and understand historical pricing trends, factors influencing those trends, and how past forecasts matched with reality. This retrospective analysis offers a comprehensive perspective on the future of solar panel pricing.
Historical Price Trends
When diving into the annals of solar panel pricing, a clear downward trajectory emerges:
- 1980s: In the early days of solar technology, the cost per watt of solar energy was approximately $20. This price was significantly prohibitive, limiting solar adoption to niche applications and research.
- 2000s: By the mid-2000s, technological advancements and greater interest in renewable energy pushed the cost down to around $3 per watt, making solar energy a more viable option for mainstream consumers.
- 2010s: Come the 2010s, and the price had dramatically fallen to just under $1 per watt, thanks to massive production scales, increased competition, and further technological improvements.
Factors That Led to Price Reductions in the Past
Several elements played pivotal roles in the price reduction journey:
- Technological Breakthroughs: Innovations in materials and manufacturing processes have consistently contributed to cost reductions. For instance, the move from thick silicon wafers to thin-film technology was a game-changer.
- Economies of Scale: As demand grew, manufacturers scaled up production, leading to decreased production costs and, consequently, reduced retail prices.
- Globalization: The rise of manufacturing hubs, particularly in China, ensured a steady supply of affordable solar panels, catering to the global demand.
- Government Policies: Many governments around the world introduced subsidies, tax breaks, and incentives, making solar installations more affordable for the average consumer.
Lessons from Past Predictions
Past forecasts, while sometimes off the mark, offer invaluable lessons:
- Overestimations: In the early 2000s, many experts believed solar prices would plateau. However, the unexpected speed of technological advancements outpaced these predictions.
- Underestimations: Conversely, some analysts in the 2010s believed that the price decline would stagnate. They underestimated the impact of massive production scales and the influence of global market dynamics.
- External Factors: External events, such as global economic recessions or abrupt policy changes, can influence solar panel pricing. For instance, trade tariffs imposed on solar panels in certain regions temporarily spiked prices.
In drawing parallels between past and future, it becomes clear that while predictions offer guidance, the solar panel market is influenced by a myriad of dynamic factors. As we anticipate prices in 2024, it's crucial to approach the topic with a blend of data-driven optimism and caution, using the past as a mirror to the future's possibilities.
Challenges to Reducing Solar Panel Prices
While the trajectory of solar panel prices has generally trended downwards, several challenges could impede or slow down further reductions. Understanding these challenges is crucial for stakeholders, from manufacturers to consumers, as they navigate the renewable energy landscape.
Raw Material Availability and Costs
Solar panels primarily consist of silicon, but they also use other critical materials like silver, aluminum, and rare earth elements.
- Silicon Shortages: Silicon, the main component in most solar panels, has experienced periodic shortages. Any future shortage could drive up its price, impacting the cost of solar panels.
- Rare Earth Elements: Certain advanced solar panels use rare earth elements to boost their efficiency. The limited availability and geopolitical issues surrounding these materials can introduce price volatility.
- Metal Prices: Metals like silver, used in solar panel connectors and cells, can be subject to price fluctuations based on global demand, mining challenges, or geopolitical tensions.
Environmental and Manufacturing Concerns
While solar panels offer a green alternative to fossil fuels, their manufacturing process presents certain challenges:
- Water Usage: Producing solar panels, especially with the dominant crystalline silicon technology, requires significant amounts of water. In water-scarce regions, this can be a concern both environmentally and cost-wise.
- Waste Management: The solar panel manufacturing process generates waste, including certain hazardous materials. Managing and disposing of this waste in an eco-friendly manner can add to the costs.
- Energy-Intensive Production: The production of solar panels, especially the purification of silicon, is energy-intensive. If this energy doesn't come from renewable sources, it can offset some of the environmental advantages of solar panels and add to production costs.
Competition from Other Renewable Energy Sources
Solar energy faces competition from other renewable sources, and this competition can influence its adoption rate and price trajectory.
- Wind Energy: Wind energy has seen substantial growth and technological advancements. In regions where wind is more prevalent than sunlight, investments might shift towards wind farms, potentially slowing down solar panel demand and innovations.
- Hydro and Geothermal: In areas with significant hydro or geothermal potential, these sources can provide consistent energy supply, potentially at lower prices than solar installations.
- Emerging Technologies: Innovations like hydrogen fuel cells or advanced nuclear reactors, if commercialized at scale, could present strong competition to solar energy, influencing market dynamics and price structures.
In conclusion, while the future of solar panels remains promising, it's essential to be cognizant of the challenges. Addressing these issues head-on will be key to ensuring that solar energy remains a viable and affordable solution for the world's energy needs.
Implications of Cheaper Solar Panels
The descent in solar panel prices has profound implications, not only for the energy sector but also for the environment and society at large. The ripple effect of affordable solar panels extends beyond mere cost savings, molding the future of global energy, environment, and socioeconomic landscapes.
Impact on the Global Energy Market
The affordability of solar panels directly challenges the traditional energy market:
- Displacement of Fossil Fuels: As solar becomes more cost-competitive, it chips away at the market share of fossil fuels. For example, coal, once the backbone of many nations' energy supplies, is increasingly being replaced by solar farms.
- Grid Parity: The concept of grid parity refers to when the cost of solar-generated electricity is equal to or less than the price of traditional grid power. Regions like parts of Southern Europe and California have already reached solar grid parity, signaling a tectonic shift in their energy markets.
- Energy Storage: The decreasing cost of solar panels has accelerated investments in energy storage solutions. As solar power generation isn't consistent throughout the day, effective and affordable storage solutions become crucial for its broad adoption.
Environmental Benefits and Climate Change Mitigation
The environmental advantages of affordable solar panels are manifold:
- Carbon Footprint Reduction: As solar panels replace fossil fuel-based power sources, the resultant drop in carbon emissions is considerable. A typical residential solar panel system can offset 3-4 tons of carbon emissions annually—the equivalent of planting over 100 trees every year.
- Conservation of Resources: Solar energy reduces the need for resource extraction, whether it's coal mining or drilling for oil. This conservation has cascading benefits for ecosystems, air and water quality, and public health.
- Mitigation of Climate Change: By reducing greenhouse gas emissions, solar energy plays a pivotal role in slowing down global warming and its associated impacts such as rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and biodiversity loss.
Socio-Economic Impacts and Job Creation
Cheaper solar panels influence societies in various positive ways:
- Job Opportunities: The solar industry has been a consistent job creator. In the U.S. alone, the solar industry employed over 250,000 individuals in 2019. With more affordable panels, this number is set to rise as installations increase.
- Energy Independence: Countries that heavily rely on importing fossil fuels can leverage affordable solar energy to reduce their dependence on foreign energy sources, ensuring more stable energy prices and enhancing national security.
- Rural Electrification: In developing countries, affordable solar panels facilitate the electrification of remote regions, bypassing the need for expensive grid infrastructure. This has profound implications for education, healthcare, and overall quality of life in these areas.
In summary, the implications of cheaper solar panels are transformative. Their potential to reshape energy markets, restore the environment, and uplift societies underscores the importance of ongoing efforts to make them more affordable and accessible to all.








