Solar Energy Impacts
Solar energy is one of the most powerful sources of energy for loads. It
improves the generation of power and
depletes carbon emissions. Uses the sun’s radiation and supports loads for homes, manufacturing industries, governments, etc. According to 2023 energy research, it supplies around
3% of the total electrical supply in the world but might increase to
20% by 2050. This is a technique that will
reduce the amount of carbon coming from fossil fuels. It also
reduces one’s living and depending on fuel. It is essential, and all worries should turn for the sun to be the primary source of electricity.
Renewable Energy Basics
Unlike fossil energies such as coal, fossil gases,
solar power cannot be exhausted. The sun is the leading source of energy in solar panels. Other sources of renewable energy are wind, hydro, and biomass. Improved technology has seen increased developments in solar energy such as
portable solar energy systems. Solar panels convert sunlight to electricity. An example of converting sunlight is the
hand-held calculator. A solar panel has PV cells and converts sunlight to electricity. Currently, solar energy is
accessible and inexpensive source: spacecom.net. Technology has
increased the efficiency of solar panels from 15% a decade ago to more than
22%. The cost of systems for solar energy has
decreased over the years.
The Solar Lifecycle
The life cycle of photovoltaic starts from
raw materials to being processed and recycled, raw materials for photovoltaic are
silicon, silver, aluminum was mined, refined, and formed to release photovoltaic cells. These cells have
unfavorable holes, and these electron-hole pairs are responsible for the generation of energy to convert into clean energy. Solar panels have a life span of between
25-30 years and can be recycled: source: solarpanelsquotes.
Evaluating the Solar Footprint
Compared to the energy generated in other ways, the
environmental footprint of solar energy is only a fraction. However, it is not without its challenges, such as
land use, water consumption, and lifecycle emissions. For example, solar farms can take up a great deal of land, although the new practice of
agrivoltaics combines agriculture with solar panels, thus allowing to optimize land use. Water usage, which is mainly employed for cleaning purposes, varies greatly. For example, California has one of the driest climates and the largest solar power clique in the US, such that water consumption is still
significantly lower than that of coal or nuclear plants. Most importantly, solar panels’ carbon footprint well subsumes their clean energy: they emit only a
fraction of CO2 while producing as much as could be concomitantly generated by coal plants. Their
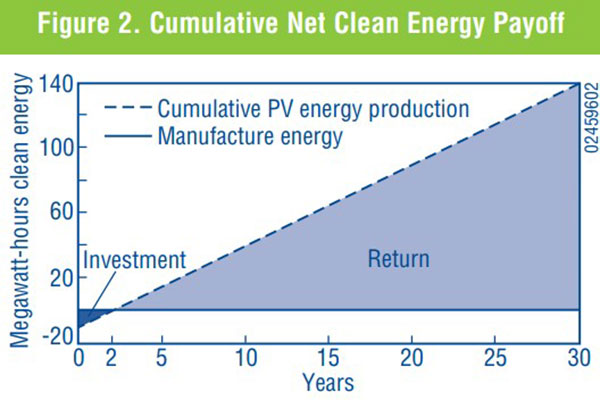
payback time is as little as
1 to 4 years.
The Economic Influence of Solar Panels
One of the reasons for the skyrocketing popularity of solar panels is that it
saps not only green but also good sense. Solar energy has the
strongest return on investment of all forms of alternative energy, such that it is not only an efficient, but also an
economically prudent choice. This is why an average American household can be expected to
save over $1,500 a year on electricity bills with solar. Considering electricity rates, it could be as much as
$30,000 in ten years, for those who manage to live in their own homes. These numbers speak for themselves and go to show the massive difference solar energy makes on the
electricity economics scene.

Cutting Energy Costs with Solar
By far the most important way solar panels affect the consumers is by
significantly cutting their electricity costs. With the panels helping to generate their own energy, the consumers are not troubled by the expenses of the utility bills. In most cases, the savings can make up to
75% of the households’ monthly energy costs alone. Solar may seem like an expensive startup, but it
pays for itself in as few as six to 10 years, thanks to the massive cuts in the energy costs and the incentives for their purchase: “cost savings figure also includes financial incentives for adopting residential solar. Many states offer tax credits and rebates that can
save thousands over the lifespan of the equipment.”
The price
According to the passage, costs of solar panel installation have
decreased over the past decade. As of the data in the passage, current solar panel installation costs range from
$15000 to $25000 of the U.S.A. after tax credits. As such, the panels’ cost depends on the size of the system and the type of the panel. The up-front cost might look high; however, the cost is absorbing with
solar loans, leases, and power purchase agreements for those who want to go solar without the investment. In addition, the
long-term savings on energy and the
increase in home value is a boon to homeowners.
The environment
Since Solar energy has
no greenhouse gas emissions, a solar panel might be seen as a blessing. Produces can rely on solar energy to stay cool. From a household roof of a home, that depends fully on solar energy, marks a
reduction of 3 – 4 pounds of carbon from carbon emission on average each year. This heat reduction effect might be seen as the results of
planting 100 trees.
Ecological Benefits of Going Solar
Besides the economic benefits, using solar energy has numerous
ecological advantages, such as reducing the amount of greenhouse gases or saving water. In comparison to coal and gas plants, solar power systems require
no water to generate electricity. Coal and gas plants withdraw
billions of gallons of water each year, which affects local ecosystems and water availability. Additionally, solar energy helps
reduce air pollution, thus helping reduce smog and dust in the air. Tackling such types of pollution is critical for
protecting ecosystems and human health.
Pollution Concerns During Manufacturer
Despite the aforementioned benefits, the
production of solar panels is not ecological. Many solar panel manufacturers claim that using solar panels has almost no environmental effect. However, the production of solar panels includes various processes and activities which involve the
emission of greenhouse gases and other types of pollution. For example, photovoltaic cells cannot be produced with the help of
nontoxic materials and elements. Furthermore, production activities involve such toxic materials, as
cadmium or lead, which have to be properly recycled in order to avoid pollution. Nevertheless, the solar industry has already initiated a number of
recycling programs and started using
less toxic materials and elements for the production of thin-film solar cells. Not only they are less toxic, but they are more efficient as well.
Land Use and Wildlife Concerns
At the same time, one of the disadvantages of using solar power systems and renewable forms of energy, in general, is
land use. In order to be equally effective, solar generators require even more land than coal plants, for example. However, building a solar plant is obviously more
environmentally friendly than a coal or gas plant. Additionally, solar panels can be placed on the
roofs of houses and parking lots. Furthermore, one is able to use the land of his or her farm to build a solar plant and turn it into a “
sunlight-sustaining, food-producing, biomass-growing haven”. A carefully planned solar farm can also provide a
safe shelter for some species of wildlife.
Functional Pros and Cons of Solar Panels
Solar panels are one of the
flagship technologies of renewable energy, with the boon of drawing power from a clean and sustainable source. Their primary function is in
decreasing the electricity bill and overall carbon footprints. However, the degree of their efficiency and functionality is a broad issue, and the factors here may include the
location, the weather conditions, as well as the
technology itself. For instance,
monocrystalline solar panels of the modern brand can achieve
20.5% and higher efficacy that makes them an efficient technology for different residential and commercial uses.

Solar Panels’ Maintenance and Longevity
One of the most attractive points of solar panels is their
low maintenance and long life. The guarantee period for solar panels typically varies from
25 to 30 years that can be even upper rated as a number of panels can work and produce electricity longer. The maintenance is typically limited to
occasional dusting of the accumulated snow, leaves, or other filth to ensure full power generation. For instance, the energy production in some states can decrease due to the rather high level of snow, and solar panels are not excepted in that case. At the same time, even this level of overall maintenance cannot be compared to the extent of it in
fossil fuel or nuclear plants.
Power Generation and Climates
One of the common concerns about solar panels is their
utility and efficaciousness in a less sunny climate. However, modern technologies have addressed the matter as the range of the solar panel’s functioning has been expanded. For example, in Germany, the solar panels are being successfully used for commercial and residential purposes despite the low level of sunny days throughout the year. However, the issue is settled due to the
proper size of the panels and the correct angle.
Problems
The main problem concerning the solar energy systems is the
problem of energy storage and the problem of space. Up to date, the costs of batteries and not efficient enough to ensure the provision of power without interruptions. While there are some advances in battery technology, the costs of the investments are still significant.


