Understanding Solar Panel Efficiency
Solar panel efficiency is a
critical parameter of the technology’s performance that defines how much sunlight is actually converted to useable electrical power. For this reason, it is
crucial to have a strong grasp of this concept when planning to launch a solar energy system, be that for residential use or at an industrial scale. To begin with, let’s outline the definition of the term
“solar panel efficiency”. It is the
proportion of sunlight that a solar panel system converts to electrical power.
Next, there are
several types of solar cells that are currently employed in such systems. Unsurprisingly, the level of efficiency varies depending on the design of the solar cell. In general, the
maximum efficiency of a common monocrystalline silicon cell is
15-20%, and that of a polycrystalline silicon one is
13-16%. The latest technologies may enable gallium arsenide cells to boast
301 efficiency levels and above. However, the utilization of such cells is associated with
higher costs, and is only appropriate in limited conditions, such as deep-space missions.
Moreover, various factors affect the efficiency of a solar panel, including the
properties of the material and its design, as well as the
operating conditions. One example of that is the fact that such panels are
less efficient at higher temperatures, which is why they are often designed with a tilt that would allow them to receive more sunlight while reducing heat. Overall, two sun-to-electricity conversion processes are conventionally distinguished in a solar panel, which are the
photovoltaic and the
concentrating solar power. The former is what the vast majority of solar cells use.
CSP, on the other hand, uses mirrors or lenses to
concentrate sunlight onto a small area of high-efficiency solar cells. This method can generate high temperatures which are used to produce steam and drive a turbine that generates electricity. While CSP systems can achieve
higher efficiencies than PV systems, they are
more complex and expensive to build and maintain.
The efficiency of the solar panels can have a
significant impact on energy output. A
higher efficiency panel will produce more electricity per square foot than a lower efficiency panel. For example, if you have two solar panels with the same size, one with
15% efficiency and the other with
20% efficiency, the latter will produce
33% more electricity. This means that if your goal is to produce a certain amount of energy, you will need
fewer high-efficiency panels than low-efficiency ones, reducing the cost of installation and maintenance and the required land. Furthermore, in places where sunlight is scarce, it would take several lower efficiency panels to produce a similar amount of energy that one panel with 20% efficiency would produce, which can be an important considerate for people who live in urban areas or do not have much space in their homes.
However, the purchase of solar panels cannot
me made solely on the efficiency results. The higher efficiency has its
clear advantages, but other parameters should be considered too, such as the
price of the panel, the
expected time of lifespan, and the
durability. With the understanding of solar panel efficiency nuances, energy consumers can make an educated decision that will maximize the amount of renewable energy produced by the money invested.

The Evolution and Efficiency of Commercial Solar Panels
It is true that the
efficiency rate of solar panels was very low in the early days. For example, efficiency rates of the first solar panels in the 1960s were around
10% to 12%. The solar panels were mainly used I space applications since they were very expensive for commercial use and other application and there were no other more efficient solar panels. However, being that people continued to research and have a lot of technological advancements there was
depletion in the efficiency of the solar panels. There was significant increase in solar panel efficiency by the 1980s. During that time, the efficiency of the solar panels was high with rates of about
14% to 16% and were much cheaper.
Pros and Cons of Rainforests
Rainforests are
ideal places for both the life of all types of animals, birds, and insects, as well as for people who come to these incredibly beautiful places to enjoy the wild and unusual nature. Rainforests are mainly in Brazil and Africa, and the most striking representative is the
Amazon jungle. People are frightened by the rainforests because they are used to dealing with the environment created by man and assigned themselves a social status higher than life – they are afraid that they will lose their prestige in the jungle and will not be able to cope without “natural benefits.” In addition, it is well known that rainforests are inhabited by
wild animals, birds, and insects: anacondas and pythons, scary caimans, aggressive jaguars and tigers, lions and leopards; many frightening and venomous snakes, huge soldiers ants, and countless other insatiable insects. On the other hand, people want to preserve life on Earth, but it is almost impossible without the preservation of rainforests. All people are connected by a
single life, and if rainforests are destroyed together with wild animals, birds and insects who will replace people to preserve the ecological balance on Earth. In addition to the flora and fauna of rainforests, there are also
vital resources for people that will be lost if people destroy the rainforests. Only people can stop the destruction of rainforests, and in order to persuade them to do this, display the rainforests in films and photographs, and allow people to decide for themselves whether it is worth saving them.
In sum, the evolution of such inventions, as commercial solar panels is impressive. Photovoltaic technology’s advancements have made it increasingly appealing to businesses and industries. The view of future developments makes solar energy a
crucial part of the worldwide transformation to more sustainable, more renewable energy sources. Material quality and design, environmental issues, and the gulf between practical situations and proffered ideal ones all concerned in solar panel efficiency. Thereby, one should understand such vital questions to optimize solar panels’ performance and proceed with monitoring to ensure panels offer the utmost energy output. Many factors might affect the output of solar panels. Thus, one should trace such aspects as
material quality and design,
environmental issues, and the
gulf between real-world and proffered ideal conditions.
Material Quality and Panel Design
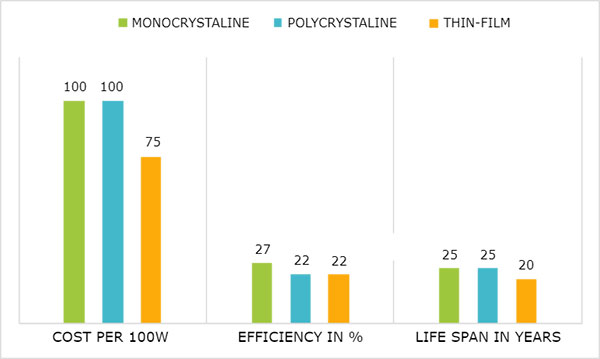
Firstly, the article highlights material quality and the design of the panels themselves as factors influencing their utility. The materials’ quality used in solar panels, primarily the materials’ crystalline structure, seems to be one of the leading determinants of panels’ efficiency. Apart from the materials’ physical quality, the silicon’s purity plays a pertinent role because high-quality silicon with fewer impurities has better electrical properties, and thus the panels are more efficient. Meanwhile, the design of solar cells also plays a highly significant role in energy efficiency. Solar cell structure is necessitated to maximize their sunlight turns into electricity. High efficiency is often observed in monocrystalline silicon solar cells. These cells are constructed of the silicon wafers made from a single crystal structure. In such a way, monocrystalline silicon solar cells possess fewer grain boundaries than polycrystalline cells. The latter are made out of multiple crystal structures and thus, have more grain boundaries and lower efficiency, normally up to 13-16% rather than up to 22% in monocrystalline cells.

The Effect of the Environment on Efficiency
Besides the technologies used, the efficiency of solar panels can also be affected by the environment in which they are installed. Several environmental factors can decrease the performance of solar panels, and some of the most significant ones include temperature, shading, and dust. Specifically, high temperatures can increase the resistance in the solar cells, which in turn may reduce their efficiency. For example, it is common for solar panels to lose about 0.5% of their efficiency for each degree above 25°C . In addition, shading, regardless of whether it is generated by the clouds, nearby trees, or the shadow of a building, can significantly reduce the output of solar panels. If only a small section of the panel is shaded, this may result in a 50% or more reduction in the output. Finally, dust and dirt on the panel can decrease the amount of sunlight that reaches the cells and reduce the efficiency of the panels. Regular cleaning and maintenance can help prevent this issue and ensure that the solar panels work to their full capacity.
In this task, I will be evaluating the difference between real world and ideal conditions, including the environmental conditions that can impact the efficiency output of a solar panel. Afterwards, I will evaluate the implications for commercial solar panels.

Conditions
The conditions for the efficiency of solar panels are usually rated with the Standard Test Conditions . These conditions are as follows:
where “STC refers to standard 1000 W/m² irradiance, 25 ’C and AM 1.5 spectrum co rresponding to a solar zenith angle of 48.19 degrees .” In the real world, these conditions may not be encountered very frequently for many different reasons. Firstly, although the sun is no less intense in the real world, environmental disturbances and weather conditions may radically reduce the apparent intensity of the sun . There are also the angles to consider as well. The sun is not directly in contact with the solar panel, and the face of the sun that the solar panel meets is usually only slightly illuminated when the sun is in either the morning or the evening . Secondly, the sun also goes through different seasons and times of day, making the contact with the solar panel erratic . Thirdly, the solar panels themselves have specific optimal perspectives that they must be viewed from to absorb the maximum amount of sunlight. Solar panels that are leaning flat against the earth that does not face the equator does not absorb as much sunlight as a solar panel that is directly against the equator. A solar panel that is not even parallel to the ground absorbing even less .
In the conclusion, therefore, provided that the factors that reduce the their efficiency and how to position them for the best sunlight have been fully recognized, these owners should be ready and equipped to take the necessary precautions to make the solar energy system operate at its optimal peak.
In general, the cost-benefit driver of efficiency is the efficiency of a commercial solar panel. The cost-benefit ratio is an aspect determined by the relationship between how much a business invests in a specific form of energy and how much it will save with the given form of energy. Greater efficiency means more output per unit of energy input. For instance, when installing a 100 kW solar system, an individual or business may need more solar panels if they are only 15% efficient. On the other hand, if the solar panels used are 20% efficient, the area will need to be smaller, and the initial investments will be less. Another Cost-benefit driver of efficiency is the cost of solar panels. Over the years the cost has continued to decrease. According to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, the average cost of solar panels has dropped by about 70% since 2010 . The cost trend combined with the efficiency trend underscores the driving rationale for solar energy’s attractiveness as an investment for businesses. This attractiveness is compounded by the government incentives in terms of tax benefits for the business and the appreciation of assets. These incentives can significantly lower payback time while increasing return on investments.
The space that a business has available for solar panel installation is a limitation for some firms, particularly in urban settings. However, even if the rooftop is relatively small, proper design and planning can help utilize the space effectively. The solar potential of a location is based on the amount of sunlight that it can receive, the orientation and tilt of the available surfaces, and any shade that they may receive from nearby objects or structures. The use of solar site assessment software can be very effective in this situation, providing businesses with the data required to establish the optimal configuration of the system. Some businesses with limited available roof space might also make use of off-site solar systems, for example, as a part of a community solar garden or a power purchase agreement, which provides businesses with the benefits of solar power without requiring installation on the site.
Another crucial consideration in the viability of this technology concerns the longevity of the equipment. Commercial solar panels typically come with a performance warranty of 25 years or more, guaranteeing that the panels will provide a certain level of efficiency throughout their operational lifetime. For example, most manufacturers today provide a linear degradation rate of 0.7% per annum, implying that after 25 years, the panels will still have a level of efficiency
above 80% of the initial . To benefit from this level of longevity, firms have to ensure that the equipment is properly installed and undergoes regular maintenance processes.
In conclusion, the utility of commercial solar panels is determined by the combination of various factors comprised of a cost-benefit analysis, the efficiency of space utilization, and the system’s life expectancy. By considering these circumstances and making use of government incentives and solar panel providers’ competition and technological improvements, businesses can decide with confidence. Thus, for businesses, the option of converting to solar is economically viable and promises benefits in the future, providing savings and a sustainable way of development. In this way, the availability of sunlight and government incentives determine the worth of commercial solar panels. The Assessed Value of the Solar Panels.
Selecting the appropriate commercial solar panels for an application is a notable choice that will affect the performance and the efficacy with which solar energy generates income. By undertaking an appraisal of the company’s space facility and comparing the effectiveness of the best-rated solar panels and their price, one can assess the quality. To satisfy all the requirements, one needs to be aware of the effectiveness of the manufacturer and their installation quality.
Based on the above considerations, the first necessity of choosing the right solar panels refers to an adequate assessment of the business per square feet energy needs. In this manner, the first step may be provided for the installation of the panels and ensuring their sustainable use. The appraisals should begin from trying to understand how much power has been used historically in the business per day and per month. In essence, the measurement of dayly was provided using the figures of 20kWh in the summer time and
15kWh – in wintertime. Then these accounts were multiplied by the number of operation days in each season, which purveyed 120 and 150 days deflecting additionally 20 %. If it is measured that annually the business consumes average consummation
per one day of 500 kWh, then the installed system should have alike characteristics to fully operate. Thus, the size and the strength will be harmonized with needed energy levels. Finally, in this measure, one should consider that there may be also different hours of maximum power utilization which enlarge the panel according to the growing offered business offer.
After the energy needs have been calculated, businesses can start comparing efficiency and cost. As stated previously, a higher efficiency panel may also mean a higher initial cost, but it would be able to generate more electricity per square foot, which would mean a quicker return on investment . However, when comparing the panels, it is important to consider the price per watt, as it is a standard unit of the solar panel cost . For example, if a first panel would cost $3.00 per watt with a 1.20$ per watt degradation rate and a second panel would cost $2.00 per watt with a 1.50$ per watt degradation rate, the end price at 350W per panel would be $1,050 and $700 for the first and second panels respectively. Thus, even though the first panel is cheaper, the second panel would be more efficient and cost-effective, as it would produce more electricity.
Furthermore, the degradation rate is another crucial factor to assess, as it might correlate to the time it takes for the panels to degrade and, thus, reduce their electricity production . For example, the first panel will only need $1,050 of the total investment to generate 350W,
but the need for 1,750$ worth of panels to achieve the same production might cancel out the advantages of a cheaper purchase. Finally, the most important factor to consider is bit the effectiveness of the panels, but also their long-term quality and efficiency, such as the quality of their manufacturer and installation company. Reputable manufacturers usually provide substantial warranties, ranging
from 10 to 25 years, which should cover the performance of the product and defects of the panels. Their record and customer reviews should also be taken into consideration, as well as the certifications of the panels . Furthermore, the quality of the installation is often just as important as the quality of the panels. The installation must be done by a certified professional and take into account the design of the system, the quality of the mounting equipment, as well as the local building codes and regulations.
On the whole, the choice of the most suitable commercial solar panels warrants a profound analysis of the amount of energy required by the company, the rates of efficiency and cost of different panels, and the credibility of the manufacturer and the contractor. As long as this consideration is done deliberately and with a profound understanding of the technology , a business is likely to benefit from solar investment and receive high-quality sustainable energy solution.



