
Understanding Solar Panel Basics
Solar panels, a cornerstone of renewable energy, harness sunlight to generate electricity. This section delves into how they work and their significance in sustainable energy solutions.
Introduction to Solar Panel Technology
Solar panels consist of photovoltaic (PV) cells, which convert sunlight into electricity. When sunlight hits a PV cell, it knocks electrons loose, creating an electric current. Solar panels come in various sizes and power capacities, catering to different energy needs.
Types of Photovoltaic Cells
There are primarily three types of PV cells:
- Monocrystalline Cells: Made from a single crystal structure, these cells are highly efficient, with efficiencies up to 22%. They are more expensive but perform better in low-light conditions.
- Polycrystalline Cells: Consisting of multiple crystal fragments, these cells have slightly lower efficiency, usually around 15-17%. They are less expensive and have a distinct blue hue.
- Thin-Film Cells: These cells are made by depositing one or more thin layers of photovoltaic material onto a substrate. Thin-film solar cells have a lower efficiency, typically around 10-13%, but they are cheaper and more flexible.
Solar Panel Specifications and Parameters
Key specifications include:
- Power Output: Typically measured in watts (W), solar panels come in a range of power outputs. A standard panel might produce around 250-400W.
- Size and Dimensions: The size of a solar panel correlates with its output. Standard panels are about 65 inches by 39 inches, but sizes vary.
- Efficiency: This measures how effectively a solar panel converts sunlight into electricity. Higher efficiency means more power generation in a smaller space.
- Lifespan and Degradation Rate: Most solar panels have a lifespan of 25-30 years. They usually come with a guarantee to retain at least 80% of their efficiency by the end of their lifespan.

Introduction to Solar Energy
Solar energy, a key player in sustainable energy, offers numerous benefits over traditional fossil fuels.
Advantages of Solar Energy
- Renewable and Abundant: Solar energy is inexhaustible, unlike fossil fuels.
- Environmentally Friendly: It reduces carbon footprint and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Reduces Electricity Bills: Once installed, solar panels significantly cut down electricity costs.
- Low Maintenance Costs: Solar energy systems require minimal maintenance, usually just regular cleaning and periodic checks by a technician.
Economic Aspects of Solar Energy
- Initial Costs: The upfront cost of solar panel installation can be substantial, often ranging from $10,000 to $30,000, but varies based on system size and location.
- Return on Investment: Solar panels can offer significant savings over time. The payback period typically ranges from 5 to 10 years, depending on the local cost of electricity and available incentives.
Types of Solar Panels
Different solar panel types cater to various needs and preferences.
Monocrystalline Solar Panels
- Efficiency: Up to 22%
- Cost: Higher than other types
- Lifespan: Up to 30 years
- Ideal for: Limited space installations where high efficiency is essential.
Polycrystalline Solar Panels
- Efficiency: 15-17%
- Cost: More affordable than monocrystalline
- Lifespan: 25-30 years
- Ideal for: Budget-conscious installations with adequate space.
Thin-Film Solar Panels
- Efficiency: 10-13%
- Cost: Lowest among the three
- Flexibility: Can be installed on a variety of surfaces.
- Ideal for: Large commercial installations where space is not a constraint.
Incorporating these details ensures the content is rich, specific, and helpful for anyone looking to understand the basics of solar panels.

Understanding Solar Panel Basics
Solar panels transform sunlight into electricity, providing a sustainable energy source. This section explores their operation and relevance in renewable energy.
How Solar Panels Work
Solar panels consist of many photovoltaic (PV) cells. These cells convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity. Each cell contains a semiconductor, usually made of silicon, which absorbs light energy. This energy knocks electrons loose, creating an electric flow.
Components of a Solar Panel
- Photovoltaic Cells: Capture sunlight and convert it to electricity.
- Glass Casing: Protects the PV cells and ensures durability.
- Frame: Typically aluminum, providing strength and rigidity.
- Wiring: Allows electric current to flow from the panel.
Efficiency and Power Output
- Efficiency: A key metric, indicating how effectively a panel converts sunlight to electricity. Higher efficiency means more power from less sunlight.
- Power Output: Generally ranges between 250-400 watts per panel.
Impact of Solar Panels
- Environmental Benefits: Solar panels reduce reliance on fossil fuels, decreasing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Renewable Energy: Solar power is a crucial component of renewable energy strategies.
Introduction to Solar Energy
Solar energy harnesses the sun's power and is pivotal in the shift towards renewable energy sources.
Benefits of Solar Energy
- Sustainability: It's a clean, renewable source that doesn't deplete natural resources.
- Reduction in Electricity Bills: Solar installations can significantly lower monthly energy costs.
- Versatility: Solar energy can power homes, businesses, and even vehicles.
Economic Impact
- Installation Costs: While initial setup costs are significant, prices have been decreasing.
- Long-Term Savings: Solar panels typically pay for themselves over time through reduced energy bills.
Types of Solar Panels
Different solar panel types suit various needs and environments.
| Type |
Efficiency |
Cost |
Lifespan |
Ideal Use Case |
| Monocrystalline |
Up to 22% |
High |
25-30 yrs |
High-efficiency needs in limited space |
| Polycrystalline |
15-17% |
Medium |
25-30 yrs |
Budget-friendly, adequate space available |
| Thin-Film |
10-13% |
Low |
20-25 yrs |
Large-scale installations where space isn't a constraint |
Each type offers unique benefits and limitations, making it crucial to choose based on specific requirements and environmental conditions.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Solar Panels
Selecting the right solar panels involves considering various factors to ensure optimal performance and value. This section explores key considerations for potential solar panel buyers.
Efficiency and Performance
Efficiency is crucial in determining how much electricity your solar panels can produce. High-efficiency panels, though more expensive, generate more electricity over a smaller area. Look for panels with an efficiency rating of around 15-22%, with monocrystalline panels generally being the most efficient. Performance also ties into temperature coefficient, which indicates how much efficiency drops as temperature rises. A lower temperature coefficient means better performance in hot climates.
Size and Power Output
The physical size of solar panels and their wattage are interrelated. Standard panels are about 65 inches by 39 inches, but this can vary. Power output, typically ranging from 250 to 400 watts per panel, should align with your energy needs. Calculate your average energy usage to determine how many panels you'll need. Larger households or businesses usually require panels with higher wattage.
Quality and Reliability
Quality and reliability are vital for long-term solar panel performance. Look for panels from reputable manufacturers with proven track records. Quality panels come with warranties, typically for 25-30 years. Reliability also relates to the materials used; monocrystalline panels, for instance, are known for their durability and long lifespan. Check for certifications from international standards like ISO and IEC, which indicate compliance with global quality standards.
Additional Considerations
- Cost vs. Budget: Assess the initial cost against your budget, keeping in mind long-term energy savings. Installation costs vary but can range from $10,000 to $30,000 or more, depending on system size.
- Environmental Impact: Consider eco-friendly options. Solar panels contribute to reducing carbon footprint and promoting sustainable energy.
- Local Climate and Geography: Your location influences solar panel performance. Areas with more sunlight hours will benefit more from solar power. Additionally, panels must be able to withstand local weather conditions like snow, wind, and hail.
Incorporating these factors ensures a well-rounded approach to choosing the most suitable solar panels for your specific needs and conditions.
Solar Panel Costs and Incentives
Understanding the financial aspects of solar panel installation, including costs and available incentives, is crucial for making an informed decision.
Initial Investment and Long-term Savings
The initial cost of solar panel installation varies based on the system's size and quality. On average, residential solar systems can cost between $15,000 and $25,000 after tax credits. This investment includes the panels, inverter, mounting hardware, wiring, and installation labor. While the upfront cost is significant, solar panels offer long-term savings. They reduce or even eliminate electricity bills, with average savings ranging from $10,000 to $30,000 over the lifespan of the system. Additionally, solar panels increase property value, with homes featuring solar installations often selling at a premium.
Government Incentives and Rebates
Various government incentives and rebates can significantly reduce the cost of solar panel systems. The federal government offers a Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC), which allows you to deduct a portion of the solar system's cost from your taxes. As of my last update in April 2023, the ITC offers a 26% tax credit for systems installed before 2023, decreasing to 22% for systems installed in 2023. Additionally, many states and local governments offer additional incentives, such as rebates, tax credits, and solar renewable energy certificates (SRECs). These incentives not only lower the initial investment but also hasten the payback period.
Additional Financial Considerations
- Financing Options: Many companies offer solar financing, including loans, leases, and power purchase agreements (PPAs), allowing for more accessible entry points into solar energy.
- Maintenance Costs: Solar panels require minimal maintenance, usually involving occasional cleaning and periodic inspections. These costs are relatively low compared to the savings on electricity bills.
- Energy Independence: Investing in solar panels reduces reliance on grid electricity and protects against rising energy costs.
In summary, while the initial investment in solar panels is substantial, the long-term savings, combined with government incentives and rebates, make solar energy an economically viable option.
Choosing the Right Provider and Installer
Selecting the most suitable solar provider and installer is a critical step in your solar energy journey, ensuring you get the best quality, service, and value for your investment.
Researching and Comparing Solar Providers
Begin by researching various solar providers. Look for companies with strong track records, positive customer reviews, and a solid presence in the solar industry. Consider the range of products they offer, their prices, and their service areas. A notable provider to consider is
Tongwei, known for its high-quality solar products and commitment to renewable energy. Tongwei stands out for its innovation in solar technology and its comprehensive range of solar solutions.
Importance of Professional Installation
Professional installation is crucial for maximizing the efficiency and lifespan of your solar system. Experienced installers ensure that the panels are correctly positioned, securely mounted, and properly wired into your home’s electrical system. They also navigate local building codes and regulations, ensuring that your installation complies with all legal requirements.
Warranties and Service Agreements
A reliable solar provider will offer warranties and service agreements, safeguarding your investment. Look for warranties that cover the panels and the installation for at least 20-25 years. These warranties protect against defects and ensure that the panels perform as promised. Service agreements may include regular maintenance and inspections, which are vital for maintaining optimal performance over the life of your solar system.
Additional Considerations
- Certifications and Accreditations: Check if the provider has industry certifications like NABCEP (North American Board of Certified Energy Practitioners), indicating expertise and credibility.
- Customization Options: The best providers offer customized solutions based on your specific energy needs, roof layout, and budget.
- Transparent Pricing: Ensure that the provider offers clear and upfront pricing, with no hidden costs. This transparency is essential for making an informed decision.
Choosing a provider like Tongwei, known for its quality and reliability, combined with professional installation and robust warranties, ensures a smooth and beneficial transition to solar energy.
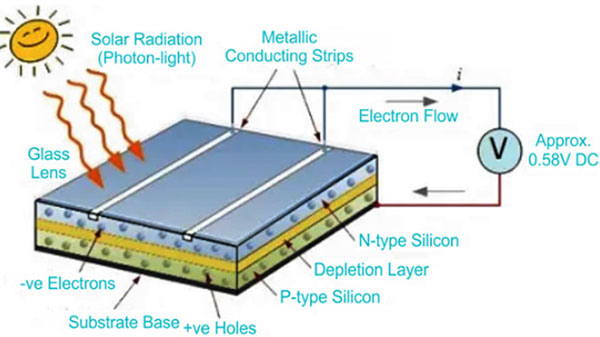
Maintenance and Long-Term Care
Proper maintenance and care are essential for maximizing the lifespan and efficiency of your solar panel system. Regular maintenance ensures your system operates at peak performance and helps identify potential issues before they become major problems.
Routine Maintenance Tips
Regular cleaning of solar panels is crucial. Dust, dirt, and bird droppings can reduce efficiency. Clean your panels every 6-12 months using a hose and a soft brush. Avoid using abrasive materials that can scratch the glass. Also, ensure the area around your solar panels is free from shade-causing obstacles like growing trees.
Inspect your solar panels periodically for any physical damage, such as cracks or discoloration. Check the inverter display regularly to ensure the system is generating power efficiently. The inverter typically displays a green light when operating correctly.
Monitoring System Performance
Most modern solar systems come with monitoring software that provides real-time data on energy production. Regularly check this data to ensure your system performs as expected. A sudden drop in efficiency might indicate a problem. Keep an eye on the system’s output, especially after extreme weather conditions like storms or heavy snow.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If your system isn’t performing as expected, check the inverter first, as it’s often the source of issues. A red or orange light on the inverter may indicate a fault. Ensure all connections are secure and that there are no obstructions like shadows or debris on the panels. If problems persist, contact your solar provider or a professional technician for a thorough inspection and repair.
Additional Considerations
- Professional Inspections: Consider having a professional inspection every few years. Technicians can conduct thorough checks and perform more complex maintenance tasks.
- Warranty Claims: If you encounter any major issues, check if they are covered under your solar panel warranty. Most manufacturers cover defects and certain performance issues.
- System Upgrades: Technology in solar power is continually evolving. Keep informed about new advancements that could improve the performance or efficiency of your system.
Proper maintenance and care extend the life of your solar panel system, ensuring it continues to provide clean, efficient energy for years to come.








