
Solar Energy Basics
Solar energy harnesses the power of the sun to produce electricity. This sustainable, renewable energy source is increasingly popular due to its environmental benefits and decreasing costs. The sun's energy, in the form of sunlight, is abundant and accessible worldwide, making it a viable energy solution for diverse applications.
What is Solar Energy?
Solar energy refers to capturing the sun's rays and converting them into usable electricity. This process involves using photovoltaic (PV) cells, which are semiconductor devices that generate electricity when exposed to sunlight.
Key Components of a Solar Energy System
A solar energy system comprises several essential components:
- Solar Panels: Devices that convert sunlight into electricity.
- Inverter: Converts the direct current (DC) from the panels into alternating current (AC) for use in homes and businesses.
- Battery Storage: Stores excess energy for use when sunlight is not available.
- Mounting and Racking System: Securely holds solar panels in place.
- Charge Controller: Regulates the voltage and current from the panels to the battery, preventing overcharging.
How Solar Panels Work
Solar panels are the heart of a solar energy system. They consist of many solar cells made from silicon, a semiconductor material. When sunlight hits a solar cell, it causes electrons in the silicon to become excited and move freely. This movement of electrons generates an electric current.
Photovoltaic Effect
The photovoltaic effect is the process of converting light into electricity. In solar cells, this effect occurs when photons from sunlight knock electrons into a higher state of energy, creating electricity.
Types of Solar Panels
Solar panels come in different types, each with unique characteristics:
- Monocrystalline Panels: Made from a single crystal structure, these panels are highly efficient but also more expensive.
- Polycrystalline Panels: Consist of multiple crystal fragments and are less efficient but more affordable than monocrystalline panels.
- Thin-Film Panels: Made by depositing one or more thin layers of photovoltaic material onto a substrate. These panels are less efficient but offer flexibility and are lightweight.
Types of Solar Energy Systems
Solar energy systems can be categorized based on their functionality and connectivity with the power grid.
Grid-Connected Systems
These systems are connected to the local electric grid and can feed excess power back to the grid. They typically do not include battery storage and rely on the grid for backup power.
- Net Metering: Allows homeowners to sell excess electricity to the utility company, offsetting their energy costs.
Off-Grid Systems
Off-grid systems are not connected to the electric grid and rely entirely on solar power and battery storage. They are ideal for remote locations without grid access.
- Battery Storage: Critical for storing energy for use during nighttime or cloudy days.
Hybrid Systems
Hybrid systems combine features of both grid-connected and off-grid systems. They are connected to the grid but also include battery storage for energy independence and backup.
System Specifications and Efficiency
- Efficiency: The efficiency of solar panels typically ranges from 15% to 22%.
- Power Output: Solar panels are commonly available in sizes ranging from 250 to 400 watts.
- Lifespan: The average lifespan of solar panels is about 25 to 30 years.
Cost Considerations
- Initial Costs: The cost of a residential solar system varies but typically ranges from $15,000 to $25,000 before incentives.
- Incentives: Tax credits and rebates can significantly reduce the upfront cost.
- Return on Investment: Solar systems can offer substantial long-term savings on electricity bills.
Environmental Impact
Solar energy is a clean, green power source that reduces greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels.
Incorporating solar energy into homes and businesses is a step towards a sustainable and environmentally friendly future. With advancements in technology, the efficiency and affordability of solar energy systems continue to improve, making them an increasingly attractive option for renewable energy.
Designing a Solar-Powered House
Designing a solar-powered house involves careful consideration of various factors to maximize energy efficiency and solar energy utilization. The goal is to create a home that not only harnesses solar power effectively but also operates efficiently to reduce overall energy needs.
Site Selection and Orientation
Choosing the right site and orientation is crucial for maximizing solar energy gain.
- Sunlight Exposure: The site should have clear exposure to sunlight, ideally with minimal obstructions like trees or buildings.
- Orientation: The house should ideally face south in the Northern Hemisphere (and north in the Southern Hemisphere) to capture the maximum sunlight throughout the year.
- Roof Angle: The angle of the roof should complement the latitude of the location to optimize the solar panel efficiency.
Integrating Solar Panels into Home Design
Incorporating solar panels into the design of the house requires strategic planning.
- Roof Design: Design the roof to support the weight of solar panels and provide ample space for installation. The roof should have a durable material that complements the solar panel system.
- Aesthetics: Integrate solar panels aesthetically into the home's design. Options like solar shingles can offer a more integrated look.
- Accessibility: Ensure easy access to solar panels for maintenance and cleaning.
Energy-Efficient Home Design Principles
Energy efficiency is key in a solar-powered house to reduce overall energy consumption.
- Insulation: High-quality insulation helps maintain a stable indoor temperature, reducing the need for heating and cooling.
- Windows: Use energy-efficient windows that minimize heat loss in winter and reduce heat gain in summer.
- Energy-Efficient Appliances: Choose appliances with high energy efficiency ratings to minimize electricity usage.
- LED Lighting: Use LED lighting, which consumes significantly less energy than traditional bulbs.
- Smart Home Technology: Incorporate smart home technologies for efficient energy management, such as smart thermostats and energy monitors.
Cost and Budgeting
- Initial Investment: The cost of a solar-powered house varies based on size, location, and design but typically ranges from $20,000 to $40,000 for the solar system alone.
- Long-term Savings: Solar-powered homes can significantly reduce or eliminate electricity bills, offering long-term savings and a shorter payback period.
Material and Quality Considerations
- Solar Panel Quality: Opt for high-quality solar panels with a good warranty, typically offering 25 to 30 years of lifespan.
- Building Materials: Use sustainable and durable building materials to ensure the longevity and efficiency of the home.
Advantages and Potential Limitations
- Environmental Benefits: Solar-powered homes significantly reduce carbon footprint and reliance on non-renewable energy sources.
- Energy Independence: These homes offer greater energy independence and protection against rising energy costs.
- Limitations: The effectiveness of solar power can be limited in areas with low sunlight exposure or during prolonged cloudy or rainy periods.
Designing a solar-powered house is a forward-thinking approach to living sustainably. It requires thoughtful planning and investment but offers significant environmental and financial benefits in the long run.
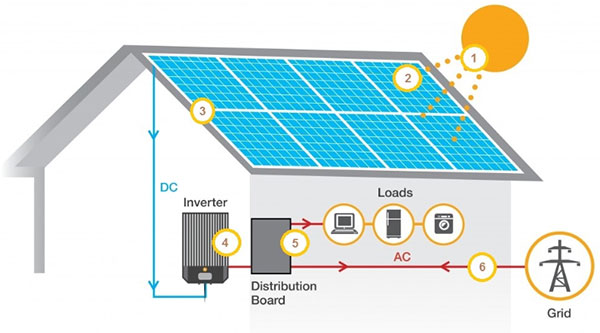
Energy Storage and Management
Effective energy storage and management are essential for maximizing the efficiency and reliability of solar-powered systems. This involves storing excess solar energy and managing its use to ensure a constant power supply, especially during periods without sunlight.
Battery Storage Systems
Battery storage systems are crucial for storing solar energy for later use.
- Types of Batteries: Common types include lead-acid, lithium-ion, and saltwater batteries. Lithium-ion batteries are popular due to their higher efficiency and longer lifespan.
- Capacity and Power Ratings: Battery capacity is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), with typical home systems ranging from 5 kWh to 20 kWh.
- Lifespan and Quality: The average lifespan of solar batteries is around 5 to 15 years, depending on the type and usage. Choosing high-quality batteries ensures longer service life and better performance.
- Cost Considerations: The cost of a solar battery system can range from $4,000 to $15,000, depending on capacity and technology.
Energy Management Systems
Energy management systems (EMS) optimize the use and distribution of stored solar energy.
- Functionality: EMS monitor energy production, usage, and storage, automatically adjusting to maximize efficiency.
- Smart Features: Advanced systems include features like predictive weather analysis to optimize energy usage based on expected sunlight.
- Integration with Renewable Sources: Some EMS can integrate with other renewable sources, like wind power, for a more comprehensive energy solution.
Backup Power Solutions
Backup power solutions provide energy during outages or insufficient solar production.
- Generators: Gasoline, diesel, or propane generators can serve as backup power sources. However, they are less environmentally friendly.
- Hybrid Systems: Combining solar with other renewable sources or generators offers a more reliable backup solution.
- Power Capacity: Backup systems should have enough capacity to power essential appliances during outages. The required capacity varies based on individual household needs.
Cost and Budgeting
- System Cost: The cost of an energy storage and management system varies greatly based on capacity, technology, and additional features.
- Energy Savings: Efficient energy storage and management can lead to significant savings on electricity bills, especially in areas with high energy rates or demand charges.
Environmental Impact
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Using solar energy and efficient storage reduces reliance on fossil fuels, decreasing carbon emissions.
- Sustainable Energy Use: These systems promote sustainable energy use by maximizing renewable energy sources.
Energy storage and management are integral to the success of solar-powered systems, providing energy security, increasing efficiency, and contributing to a more sustainable future. The choice of storage systems, along with smart management solutions, plays a pivotal role in the effectiveness of solar energy utilization.

Case Studies
Analyzing real-world case studies of 100% solar-powered homes provides valuable insights into the practical application, challenges, and successes of such projects. These studies demonstrate the feasibility and benefits of relying solely on solar energy for residential needs.
Real-World Examples of 100% Solar-Powered Homes
Several homes around the world serve as exemplary models of complete solar reliance.
- Example 1: California Solar House - This home features a 10 kW solar panel system, capable of generating approximately 14,600 kWh per year. The house includes energy-efficient appliances, LED lighting, and a smart home system for energy management. The total cost for the solar setup was around $30,000, but with state incentives and tax rebates, the effective cost reduced significantly.
- Example 2: German Solar-Powered Home - In Germany, a house utilizes a 7 kW solar panel system along with a 14 kWh battery storage unit. This setup provides sufficient energy for the household's needs, even during the winter months. The total investment for this system was approximately €25,000 ($29,000), with a payback period of around 10 years.
- Example 3: Australian Off-Grid Home - An off-grid house in Australia operates on a 15 kW solar panel system with a 40 kWh battery storage capacity, ensuring continuous power supply even during cloudy days. The system cost was about AUD 50,000 ($36,000), and it saves the homeowner approximately AUD 3,000 ($2,160) annually in energy costs.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices
The following lessons and best practices emerge from these case studies:
- Importance of Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy-efficient designs and appliances significantly reduces the overall energy requirement, making it easier and more cost-effective to rely on solar power.
- Adequate Storage is Key: Sufficient battery storage is essential to maintain a consistent power supply, especially in areas with less predictable sunlight.
- Regular Maintenance: Regular maintenance of solar panels and batteries ensures optimal performance and longevity of the system.
- Planning for Future Needs: Designing the system with future expansion or increased energy needs in mind allows for easier upgrades.
- Utilizing Incentives: Taking advantage of government incentives and tax rebates can significantly reduce the initial investment cost.
Through these case studies, it becomes evident that with proper planning, investment, and utilization of available technology and incentives, 100% solar-powered homes are not only feasible but also economically viable and environmentally sustainable. These real-world examples serve as benchmarks and learning sources for future solar home projects.

Sustainable Living and Environmental Impact
Sustainable living involves making choices that reduce one's environmental impact, and it starts at home. By adopting practices that conserve resources and minimize pollution, homeowners can significantly contribute to a healthier planet.
Reducing Carbon Footprint
A carbon footprint represents the total amount of greenhouse gases produced to support human activities, typically expressed in equivalent tons of carbon dioxide (CO2).
- Solar Power Adoption: Installing solar panels significantly reduces reliance on fossil-fueled electricity, thereby cutting down CO2 emissions. For instance, a typical residential solar panel system can reduce carbon emissions by approximately 3 to 4 tons per year.
- Energy Efficiency: Enhancing home energy efficiency through upgraded insulation, energy-efficient appliances, and LED lighting further reduces the carbon footprint.
- Sustainable Transportation: Using electric vehicles powered by solar energy can further decrease CO2 emissions.
Other Sustainable Practices for Homeowners
Besides solar energy, numerous other practices contribute to sustainable living:
- Water Conservation: Installing low-flow fixtures and harvesting rainwater for use in gardens and toilets helps conserve water.
- Recycling and Composting: Proper waste management, including recycling and composting, reduces landfill waste and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Using sustainable, recycled, or rapidly renewable materials in home construction and renovation lowers the environmental impact.
Future Trends in Solar Energy
The solar energy sector is evolving rapidly, with several trends shaping its future:
- Increased Efficiency: Ongoing research aims to enhance the efficiency of solar panels, potentially surpassing the current average efficiency of 15-20%.
- Cost Reduction: As technology advances, the cost of solar installations continues to decrease, making solar energy more accessible.
- Innovative Technologies: Emerging technologies, like building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV), combine solar technology with building materials, offering more aesthetic and efficient ways to integrate solar power into homes.
- Energy Storage Innovations: Advances in battery technology are making energy storage more efficient and affordable, enabling more homes to rely entirely on solar power.
- Smart Grid Integration: Future solar systems will increasingly integrate with smart grid technology, allowing for more efficient energy distribution and management.
Adopting sustainable practices and leveraging the advancements in solar energy technology are key to reducing environmental impact and promoting a healthier planet. As technology progresses, the feasibility and appeal of solar energy and sustainable living continue to increase, offering a promising outlook for the future.








